MBSA (Model-Based Safety Assessment or Analysis) represents a set of techniques which model systems, from both functional and dysfunctional points of view, in order to analyze their safety properties. MBSA uses failure propagation models (FPM), in this case with the AltaRica language, the method defined below and the CECILIA Workshop tool.
MBSA is recognized in international aeronautical standards as a means of demonstrating safety objectives within the meaning of CS xx.1309 (SAE ARP4761A / EUROCAE ED-135A).
AltaRica
AltaRica is a language born in 1998 from a collaboration between research, mainly at the Laboratoire Bordelais de Recherche en Informatique (LaBRI), and industry. This language, based on formal methods, has been designed and developed for qualitative and quantitative safety analysis. One version of the language, called AltaRica Data-Flow, is implemented in the CECILIA Workshop tool.
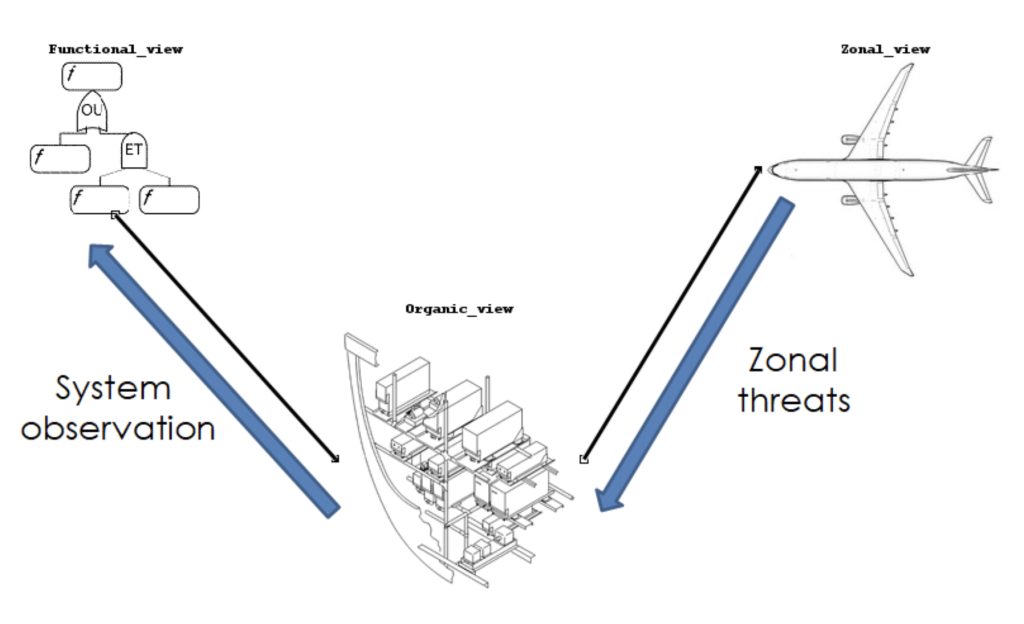
Method
Any modeling is the result of the triptyc language / method / tool. An MBSA modeling method is therefore proposed, with its objectives, principles and rules. It can be adapted to suit different fields and problems. The “MBSA for professionals” training course aims to explain and implement this method, based on a generic public library and equipped with CECILIA Workshop.
Models
Some examples of public models are provided in this section. They come both from research (IRT projects, ONERA…) and industry (SATODEV, ARP4761 standard…). Two Cecilia libraries, one Boolean and the other generic, are also available.